YEAR 2023
Inter-task project Assessment of successes and lessons learned for biofuels deployment
 Download | September 2023 | “Sustainable biomass supply chains for international markets”
Download | September 2023 | “Sustainable biomass supply chains for international markets”
Report Work package 4
The report presents case studies for feedstock supply chains that have been evaluated from multiple viewpoints as these are vital for successful development of advanced biofuels. It highlights lessons from biorefineries and pulp mills using short rotation wood fibre crops (Brazil), European experiences in development of bio-based supply chains for torrefied woody biomass, pioneer biorefineries in the US (traditional feedstock pre-processing for herbaceous feedstocks) and conceptual depots producing conversion-ready feedstock and co-products.
Regional Transitions project 1.0
 Download | August 2023 | “Regional transitions in existing bioenergy markets”
Download | August 2023 | “Regional transitions in existing bioenergy markets”
Synthesis report of IEA Bioenergy Task 40 Regional Transitions project 1.0
Results of a project in which IEA Bioenergy Task 40 experts explored strategies for developing sustainable bio-based value chains in a regional dynamic market context. The focus was on feedstock supply chains, a cornerstone for the development of sustainable and reliable bio-based value chains, and was organised into three activities:
- Regional transitions – trends in the European Union and a case study for Germany
- Strategies to increase the mobilization and deployment of local (endemic) low value heterogenous solid biomass resources
- Adoption of bioenergy by existing agriculture and forestry biomass feedstock suppliers in the United States
Biomass & bioenergy IEA bioenergy: Update 72
Open-access paper available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S096195342200246X
Paul Bennett, Jan Liebetrau, Uwe Fritsche, Biomass & bioenergy IEA bioenergy: Update 72, Biomass and Bioenergy, Volume 168, 2023, 106584, ISSN 0961-9534, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2022.106584.
Deployment of BECCUS value chains in the United States

Download | January 2023 | A case study of sequestering CO2 from ethanol production
Contribution of IEA Bioenergy Task 40 to the IEA Bioenergy inter-task project Deployment of BECCUS value chains
The Archer Daniels Midland Company (ADM), in collaboration with a consortium of academic, industry, and national laboratory partners, have studied the potential for sequestering CO2 generated from an ethanol production plant at multiple sites in the Illinois Basin. The two projects represented in this case study include the Illinois Basin Decatur Project (IBDP) which represents a large-scale geologic test to inject one million metric tons (mt) of CO2 over a three-year period (1,000 mt/day) and the Illinois Industrial CCS project (IL-ICCS) targeted to demonstrate advanced CCS technologies at industrial scale facilities and inject and store one million mt of CO2 per year (3,000 mt/day). The demonstrations were coupled with development of the Intelligent Monitoring System (IMS) program to develop and validate software tools.
This case study is part of a series of studies carried out under the Deployment of BECCS/U Value Chains project with the aim to highlight sector-specific characteristics. More case studies and reports available here.
YEAR 2022
Deployment of BECCUS value chains
Synthesis report “From concept to commercialization”
Over the duration of the 2019-2021 IEA Bioenergy triennium, a consortium of IEA Bioenergy Tasks – Task 36, Task 40, Task 44 and Task 45 – collaborated on an inter-task project called Deployment of BECCUS value chains, led by Task 40. The objective of the project was to improve the understanding of the opportunities for, and obstacles to, deployment of bioenergy combined with carbon capture and utilization or permanent storage (BECCUS). All in all, seven publications have been produced as project outputs. This report includes a summary and a synthesis of these individual studies, as well as a discussion and an outlook into questions to be further explored in future research. More case studies and reports available here.
Bioeconomy Synergies Project

Download | June 2022 | Progress & Prospect Report 2019-2021
This document explains scientific findings from the internal Task 40 project on Circular Bioeconomy, in particular with the following outputs:
- Provide case studies of synergies between food/feed, material and energy uses of biomass
- Create a first version of a resource flow database for modelling synergies in a Circular Bioeconomy
- Derive insights for bioeconomy supply network modelling, policy recommendations and the strategic direction of the IEA Bioenergy Task40 including follow-up projects
BECCS – Delivering negative emissions: implications for the (bio)energy system
IEA Bioenergy inter-task project Deployment of bio-CCUS value chains
Presentation at 30th European Biomass Conference & Exhibition, online, 9th – 12th May 2022
Renewable gas ‐ deployment, markets and sustainable trade (Intertask project)
The main objective of the project was to enable more deployment of renewable gases and to underpin their sustainability. It was carried out in collaboration with IEA Hydrogen, EC DG ENER and industrial partners, and was completed in March 2022.
Click here to view the project and results.
- Summary report
- Biomethane – factors for a successful sector development. Synthesis Report of WP1
- Renewable gas and CCU – Contribution to WP1
- Status and perspectives of non-biogenic renewable gases – Synthesis Report of WP2
- Sustainable potentials for renewable gas trade – Synthesis Report of WP3
Carbon accounting in Bio-CCUS supply chains – identifying key issues for science and policy
 Download | February 2022 | Intertask project “Deployment of Bio-CCS/CCU Value Chains” contribution of IEA Bioenergy Task 40/45.
Download | February 2022 | Intertask project “Deployment of Bio-CCS/CCU Value Chains” contribution of IEA Bioenergy Task 40/45.
Bio-CCUS (bioenergy with carbon capture and utilization or storage), is increasingly becoming a matter of on-the-ground deployment. However, while the technological aspects of capture, utilization and storage of biogenic CO2 are rather well understood and have in many cases already been used in commercial settings, there are still substantial gaps on the policy and governance side. Particularly important aspects here are carbon accounting, how to quantify the climate impact of Bio-CCUS systems and how to include these elements in policy frameworks. This report – developed by IEA Bioenergy Task 45 (Sustainability) and Task 40 (Deployment) – reviews key issues to focus on and discusses different options for how these could be addressed from a scientific as well as from a policy perspective.
Renewable Gases – Hydrogen in the Grid
 Download| January 2022 | Task 41 Special Project report
Download| January 2022 | Task 41 Special Project report
The project’s objective is to carry out a thorough study on renewable gases (RG) and the effect of hydrogen (H2) addition in the gas grid as well as applications at increased concentrations up to 100%.
Strategies for the Mobilization and Deployment of Local Low-Value, Heterogeneous Biomass Resources for a Circular Bioeconomy
Open-access paper available at: https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/15/2/433/htm
Schipfer, Fabian; Pfeiffer, Alexandra; Hoefnagels, Ric (2022): Strategies for the Mobilization and Deployment of Local Low-Value, Heterogeneous Biomass Resources for a Circular Bioeconomy. In: Energies 15 (2), S. 433. DOI: 10.3390/en15020433.
With the Bioeconomy Strategy, Europe aims to strengthen and boost biobased sectors. Therefore, investments in and markets of biobased value chains have to be unlocked and local bioeconomies across Europe have to be deployed. Compliance with environmental and social sustainability goals is on top of the agenda. The current biomass provision structures are unfit to take on the diversity of biomass residues and their respective supply chains and cannot ensure the sustainability of feedstock supply in an ecological, social and economical fashion. Therefore, we have to address the research question on feasible strategies for mobilizing and deploying local, low-value and heterogeneous biomass resources.
YEAR 2021
Decarbonizing industrial process heat: the role of biomass

Download| December 2021 | IEA Bioenergy Intertask project on industrial process heat
This report highlights the opportunities for bioenergy technologies to deliver heat in industry and compares it with alternatives for decarbonisation such as CCS, electrification and hydrogen. The report provides specific policy recommendations to accelerate its adoption.
More information and case studies on the project website
Deployment of bio-CCS in the cement sector: an overview of technology options and policy tools
Download| December 2021 | Contribution of IEA Bioenergy Task 40/45 to the Inter-task project “Deployment of Bio-CCS/CCU Value Chains”
This report reviews the prospects for implementation of CCS in the cement sector. Particular attention is given to the opportunities of combining this with the use of biogenic fuels for process heat, so-called BECCS or bio-CCS. Bio-CCS could prove to be a vital tool to make cement production with net-zero CO2 emissions possible and could potentially also enable “negative emissions”, also referred to as carbon dioxide removal (CDR). In addition to a thorough review of the technological options at hand, the report also discusses the business and policy aspects that need to be put in place to enable this.
Regional transitions in existing bioenergy markets
Open-access paper available at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0360544221014833?via%3Dihub
Burli, P. et al. (2021) Farmer characteristics and decision-making: A model for bioenergy crop adoption. Energy 234: 121235 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.121235
Highlights:
- Farmer adoption rates vary widely for crop residues and energy crops.
- Social networks and market structure influence adoption for both feedstocks.
- Information dissemination has a positive impact for energy crop adoption.
- Combining interventions can accelerate farmer adoption substantially.
Country reports: Implementation of bioenergy in Germany – 2021 update
October 2021
Biomethane – factors for a successful sector development. Synthesis Report of WP1
 Download| June 2021| First report of Intertask project “Renewable gas ‐ deployment, markets and sustainable trade”
Download| June 2021| First report of Intertask project “Renewable gas ‐ deployment, markets and sustainable trade”
The main objective of the project was to enable more deployment of renewable gases and to underpin their sustainability. It was carried out in collaboration with IEA Hydrogen, EC DG ENER and industrial partners, and was completed in March 2022. Click here to view the project and results.
Deployment of Bio-CCS/CCU Value Chains
The IEA Bioenergy project “Deployment of Bio-CCS/CCU Value Chains” strives to provide insights about the opportunities and challenges pertaining to taking Bio-CCS/CCU from pilots to full-scale projects. Case studies provide deeper insights into the key aspects that come into play for companies that are in the process of setting up value chains for capture, transportation and sequestration or utilization of biogenic CO2. A first set of case studies has been finalized, focused on integrating CCS in central biomass based heat and/or power production:
May 2021
- Biomass based combined heat and power (CHP) – HOFOR Amager CHP, Copenhagen, Denmark
- Bioelectricity – Drax Power Station, United Kingdom
- Waste-to-Energy – Fortum Oslo Varme (FOV), Oslo, Norway
 |
 |
 |
YEAR 2020
Fabian Schipfer, Lukas Kranzl, Olle Olsson, Patrick Lamers, European residential wood pellet trade and prices dataset, Data in Brief, Volume 32, 2020, 106254, ISSN 2352-3409, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2020.106254. (http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352340920311483)
Fabian Schipfer, Lukas Kranzl, Olle Olsson, Patrick Lamers, The European wood pellets for heating market – Price developments, trade and market efficiency, Energy, Volume 212, 2020, 118636, ISSN 0360-5442,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118636. (http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0360544220317448)
Roles of bioenergy in energy system pathways towards a “well-below-2-degrees-Celsius (WB2)” world (Intertask project)

Download| July 2020 | Workshop report and synthesis of presented studies
A Strategic Inter-Task Study carried out with cooperation between IEA Bioenergy Tasks 40, 43, 44 and 45
Under the IEA Bioenergy Inter-task project ‘The Role of Bioenergy in a WB2/SDG world’, a workshop was held in Berlin, on 25 November 2019. The objective of the workshop was to examine, synthesize and disseminate information from recent studies that investigate how bioenergy and associated technologies may contribute to achieving the reductions in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions that are needed to meet the WB2 target. The report summarises the workshop contributions and discussions, assesses the role of bioenergy in WB2 strategies, identifies the current state of knowledge as well as gaps in knowledge that need to be addressed.
Deployment of BECCS/U value chains
Technological pathways, policy options and business models

Download| It is becoming increasingly clear that substantial amounts of negative emissions – essentially, the removal of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere – will likely be required if global climate change is to be limited to 2°C above pre-industrial levels. Among the different negative emissions options, bioenergy with carbon capture and storage, or BECCS, is arguably one of the most commonly discussed in climate policy debates.
This report focuses on the potential and challenges associated with deploying BECCS systems and value chains in the near to medium term. It provides a brief overview of different technological options for capture, transport and storage of CO2, and offers insights into how BECCS business models could be set up. Furthermore the role of public policy in this setting is discussed, and how bioenergy with carbon capture and utilization (BECCU) could play a role in enabling BECCS deployment.
YEAR 2019
Open-access paper, available at: https://energsustainsoc.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13705-019-0225-0
Mai-Moulin, T., Fritsche, U.R. & Junginger, M. Charting global position and vision of stakeholders towards sustainable bioenergy. Energ Sustain Soc 9, 48 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13705-019-0225-0
Stakeholder’s position of bioenergy sustainability is important for the deployment and contribution of bioenergy to sustainable development. Existing publications are usually limited to specific geographical contexts and focuses. This paper aims more broadly to examine the position and vision of a wider range of stakeholder groups towards bioenergy and its development at a global level.
The work was part of the IEA Bioenergy project “Measuring, governing and gaining support for sustainable bioenergy supply chains”. More info available at: http://itp-sustainable.ieabioenergy.com/
Margin potential for a long-term sustainable wood pellet supply chain

Main report| The existing wood pellet markets face increasing competition – both the large-scale use for co-firing with coal or standalone bio-powerplants (price pressure from other low-carbon electricity technologies) and the residential use (competition from e.g., district heating, heat pumps, biogas and biomethane, as well as renewable power-to-gas). On the other hand, wood pellets are seen as key supply option for Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS), and Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Use (BECCU) which may be needed to achieve net-negative greenhouse gas emissions. Given this background, the study presents a cost baseline for pellets, analyzes potential supply cost reductions, and evaluates the future market prospects of wood pellets in industrial low- and high-temperature heat, industrial processes (e.g. steelmaking), and for BECCS/BECCU.
| Summary | Annexes |
“The future of biomass and bioenergy deployment and trade: a synthesis of 15 years IEA Bioenergy Task 40 on sustainable bioenergy trade”
The paper is published as a feature article in a special issue of the Journal Biofuels, Bioproducts & Biorefining (BioPFR), Volume 13, Issue 2 (March 2019) https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/bbb.1993
Socio-economic assessment of the pellets supply chain in the USA
 Download | In the USA, the pellet production to export has reached 5 Million tons in the last years providing positive socio-economic impacts in the regions but also some socio-economic issues that need to be further improved. The main aim of this report was to understand the dynamics between local development and forestry activities related to the production and export of pellets on local communities. The forest sector in the USA shows few signs of development vector. Income increases slowly, but steadily in the United States, but the forest sector does not follow this same path. Job creation was clearly affected between 2000 and 2010 in the USA in the feedstock production and with no signs of general improvement between 2010 and 2014, but improvements are seen in the transformation sector. This could provide better opportunities for the expansion and adaptation of the pellet sector.
Download | In the USA, the pellet production to export has reached 5 Million tons in the last years providing positive socio-economic impacts in the regions but also some socio-economic issues that need to be further improved. The main aim of this report was to understand the dynamics between local development and forestry activities related to the production and export of pellets on local communities. The forest sector in the USA shows few signs of development vector. Income increases slowly, but steadily in the United States, but the forest sector does not follow this same path. Job creation was clearly affected between 2000 and 2010 in the USA in the feedstock production and with no signs of general improvement between 2010 and 2014, but improvements are seen in the transformation sector. This could provide better opportunities for the expansion and adaptation of the pellet sector.
Transboundary flows of woody biomass waste streams in Europe

Download| The report focuses on trans boundary shipment flows of solid biomass waste, particularly wood waste (hazardous and non-hazardous), in the north-western part of Europe in the years 2010-2016. Non-hazardous wood waste is a rather cheap fuel in comparison to other solid biomass resources and hence is used in some countries for bioenergy production on a significant scale. Also, large amounts of hazardous wood waste are traded, but an overview of these trade flows is so far lacking in literature. An analysis of its trans boundary shipment can be helpful for the national plans of the countries involved as well as the industries and organizations. Next to the valorisation as material, wood waste is being used for producing energy in modern bioenergy plants in Germany, The Netherlands and Sweden. The main importers of both hazardous and non-hazardous wood waste are Germany and Sweden with a yearly import of 600+ kilotonnes (KT). The main exporters of non-hazardous wood waste are UK, The Netherlands and Norway.
YEAR 2018
PhD thesis, Svetlana Proskurina: International trade in biomass for energy production – the local and global context
 The main aim of the thesis is to increase knowledge, insights and understanding of trade of biomass, and how is it developing, in order to facilitate the growth of biomass markets globally and locally. The thesis focuses on the status of biomass trade for energy in the global and local EU-Russia context. Within in the local EU-Russia context it is possible to show the international biomass trade streams in details. Europe is currently the major player in global biomass trade and Russia is one of the leading exporters of wood pellets to the EU. Wood pellets are the main traded solid biofuel, thus its market can be studied in more detail. The thesis presents a global overview of trade in solid and liquid biofuels, particularly wood pellets, biodiesel, and bio-ethanol, and biomass products such as industrial roundwood. The thesis presents the main production, export and import volumes of studied products as well as global trade streams including potential developments of emerging trade streams such as torrefied biomass. In addition, the thesis describes the role of bioenergy in renewable energy development in the EU, and in the local context, wood pellet markets in Finland and Russia.
The main aim of the thesis is to increase knowledge, insights and understanding of trade of biomass, and how is it developing, in order to facilitate the growth of biomass markets globally and locally. The thesis focuses on the status of biomass trade for energy in the global and local EU-Russia context. Within in the local EU-Russia context it is possible to show the international biomass trade streams in details. Europe is currently the major player in global biomass trade and Russia is one of the leading exporters of wood pellets to the EU. Wood pellets are the main traded solid biofuel, thus its market can be studied in more detail. The thesis presents a global overview of trade in solid and liquid biofuels, particularly wood pellets, biodiesel, and bio-ethanol, and biomass products such as industrial roundwood. The thesis presents the main production, export and import volumes of studied products as well as global trade streams including potential developments of emerging trade streams such as torrefied biomass. In addition, the thesis describes the role of bioenergy in renewable energy development in the EU, and in the local context, wood pellet markets in Finland and Russia.
The findings presented in the thesis are the outcome of seven articles presented in the second part of the work. The thesis comprises an introduction providing the background to the research questions, followed by individual papers considering various aspects of biomass in renewable energy, the wood pellet business, and the global trade in biomass.
The findings from the work indicate that due to the variety of available biomass resources and continuing supportive policy and regulation in many countries, biomass trade will continue to be an important aspect of renewable energy markets for the foreseeable future. Despite slow progress in bioenergy development encountered in several EU countries, currently the EU remains a leader in biomass utilization and trade. Based on the example of the Finnish and Russian markets, it is evident that wood pellet markets vary considerably in different countries and have different orientations. Thus, the study concludes that fertile ground exists for further development of international trade in biomass for energy production.
The thesis could be found at: http://lutpub.lut.fi/handle/10024/158444
Biomass pre-treatment for bioenergy – Case study 1: Biomass Torrefaction
This report analyses the effects of pretreatment on supply chain efficiency by comparing the energy consumption along the supply chain of White Wood Pellets (WWP) supply with Torrefied Wood Pellet (TWP) supply.
While WWP have become a global standard energy commodity in the recent decade, TWP are just at the beginning of the industrial implementation phase. TWP are made using the same raw material as WWP, implementing an almost similar machinery set up with the additional roasting of biomass to increase the energy density (22,2 GJ/mt instead of 17,56 GJ/mt taken as industry average values) and improve the handling, storage and grinding properties.
Whether energy can be saved across the supply chain by producing torrefied wood pellets instead of white wood pellets depends on the balance between increased processing energy consumption and decreased transport energy consumption. For the supply chain analysed in this study, from Indonesia to Japan, overall energy savings of 6.7% at minimum can be reached by shifting from WWP to TWP, resulting from a 16% increase in bioenergy, used for drying and torrefaction, a reduction in the consumption of liquid fossil fuels of 20.9% (Diesel, MDO and IFO) and a 2.3% reduction of electricity consumption on MJ/GJ supplied basis. The energy reduction across the chain results in a 10.3% GHG emission reduction for TWP compared to WWP.
More information can be found at:
Building a Biorefinery Business: Strategies for Successful Commercialization

Download|This study aims to explore and analyze which barriers to commercialization can be successfully overcome by biorefineries, and which may require support from additional actors within the system, such as policy makers. The study found that when building a biorefinery business, it is crucial to decide the kind of strategy and corresponding business model to implement. Careful attention needs to be paid to the ability to mobilize biomass resources and to establish supply and demand structures at the same time. A collaborative approach, leveraging resources and building a web of favorable system components, has proven a viable strategic approach towards developing and commercializing biorefineries.
YEAR 2017
Socio-economic assessment of forestry production for a developing pellet sector: The case of Santa Catarina in Brazil.
 Download | In Brazil, the forestry sector grew strongly due to a very low starting point and shows positive results in its development, which could be explained by the close relationship between the forestry industry and the local communities. Selected criteria, index and indicators were applied in a selected region in Santa Catarina, Brazil. The secondary data was gathered from industry and government sources and combined with primary data gathered from in-depth interviews and visits to the region. In Santa Catarina there is availability of resources from the forestry production but the pellet production sector is yet incipient and mainly for regional use. Santa Catarina represents 8.5% of the country’s total planted forests, having 82% of that area covered with pine. Wood production mainly supplies the pulp and paper industry, as well as the timber industry. More specifically, the area studied in this report (Lages) represents 60% of the wood production in the state.
Download | In Brazil, the forestry sector grew strongly due to a very low starting point and shows positive results in its development, which could be explained by the close relationship between the forestry industry and the local communities. Selected criteria, index and indicators were applied in a selected region in Santa Catarina, Brazil. The secondary data was gathered from industry and government sources and combined with primary data gathered from in-depth interviews and visits to the region. In Santa Catarina there is availability of resources from the forestry production but the pellet production sector is yet incipient and mainly for regional use. Santa Catarina represents 8.5% of the country’s total planted forests, having 82% of that area covered with pine. Wood production mainly supplies the pulp and paper industry, as well as the timber industry. More specifically, the area studied in this report (Lages) represents 60% of the wood production in the state.
Global Wood Pellet Industry and Trade Study 2017
 Download | The report Global Wood Pellet Industry Market published in 2011 has always been the most downloaded document of IEA Bioenergy Task 40. We have decided to update the report and bring new insights on market trends and trade of the global wood pellets.
Download | The report Global Wood Pellet Industry Market published in 2011 has always been the most downloaded document of IEA Bioenergy Task 40. We have decided to update the report and bring new insights on market trends and trade of the global wood pellets.
The global wood pellet market has increased dramatically since 2011, with an average increase
rate of 14% per year. New countries have entered the market for both, pellet production (such as those from South-East Europe) and pellet consumption (such as East Asia). Also the global wood pellet trade increased. Intercontinental flows are dominated by the trade relation between the U.S. and the UK, while the non-industrial use is still mainly an intra-European business.
YEAR 2016
The European wood pellet market for small-scale heating
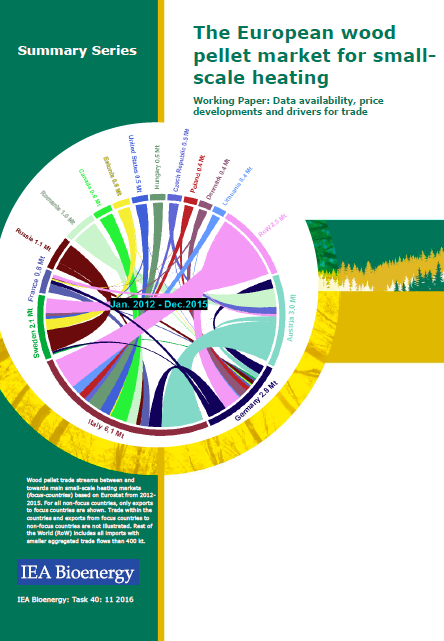 Download | This short paper summary highlights the findings of an extensive quantitative wood pellet market analysis based on trade flow data, price developments over time, exchange rate fluctuations and temperature data. Its focus lies on the main European small-scale heating countries Italy, Germany, Sweden, France and Austria in the time period January 2012 until December 2015. Market parties have been consulted to get anecdotal evidence and expert opinions to help interpret the results. The summary describes and analyses (1) the current market status with regards to internationally traded volumes of wood pellets and potentially underlying drivers as well as (2) the general state of the market for wood pellets for small-scale heating regarding international market integration and other market characteristics. Its aim is to discern key market drivers, especially when it comes to interactions between national markets. Conclusions with regards to data availability, research gaps, detectable trade patterns and wood pellets commoditisation process limitations are outlined. A webinar for interested researchers, market actors and policy makers will be scheduled for the early 2017.
Download | This short paper summary highlights the findings of an extensive quantitative wood pellet market analysis based on trade flow data, price developments over time, exchange rate fluctuations and temperature data. Its focus lies on the main European small-scale heating countries Italy, Germany, Sweden, France and Austria in the time period January 2012 until December 2015. Market parties have been consulted to get anecdotal evidence and expert opinions to help interpret the results. The summary describes and analyses (1) the current market status with regards to internationally traded volumes of wood pellets and potentially underlying drivers as well as (2) the general state of the market for wood pellets for small-scale heating regarding international market integration and other market characteristics. Its aim is to discern key market drivers, especially when it comes to interactions between national markets. Conclusions with regards to data availability, research gaps, detectable trade patterns and wood pellets commoditisation process limitations are outlined. A webinar for interested researchers, market actors and policy makers will be scheduled for the early 2017.
The presentation of the webinar The European Wood Pellet For Small-Scaling Heating can be downloaded: here. The link to the recorded session is below:
http://cif-ifc.adobeconnect.com/p1riuue4kbi/
Developing the Global Bioeconomy: Technical, Market, and Environmental Lessons from Bioenergy
 Purchase | This book reviews the bioenergy sector and draw useful lessons for the full deployment of the bioeconomy. As expectations that a future bioeconomy will rely on a series of tradable commodities, this book provides a central accounting of the state of the discussion in a multidisciplinary approach that is ideal for research and academic experts, and analysts in all areas of the bioenergy, biofuels, and bioeconomy sectors, as well as those interested in energy policy and economics.
Purchase | This book reviews the bioenergy sector and draw useful lessons for the full deployment of the bioeconomy. As expectations that a future bioeconomy will rely on a series of tradable commodities, this book provides a central accounting of the state of the discussion in a multidisciplinary approach that is ideal for research and academic experts, and analysts in all areas of the bioenergy, biofuels, and bioeconomy sectors, as well as those interested in energy policy and economics.
Mobilisation of Forest Bioenergy in the Boreal and Temperate Biomes: Challenges, Opportunities, and Case Studies
 Purchase | The book features input from key international experts who identify and analyze the main opportunities and roadblocks for the implementation of sustainable forest biomass supply chains in the boreal and temperate regions. . It also proposes recommendations for practitioners, policymakers, and future research in the field of bioenergy conversion and management, as well as those interested in sustainable management of natural resources.
Purchase | The book features input from key international experts who identify and analyze the main opportunities and roadblocks for the implementation of sustainable forest biomass supply chains in the boreal and temperate regions. . It also proposes recommendations for practitioners, policymakers, and future research in the field of bioenergy conversion and management, as well as those interested in sustainable management of natural resources.
 Cascading of woody biomass: definitions, policies and effects on international trade
Cascading of woody biomass: definitions, policies and effects on international trade
Download | Cascade use or “cascading” of woody biomass is increasingly being discussed as a key principle upon which to base efficient utilization of wood, especially in the European Union (EU). Cascading does not have one universal definition, although a common theme is that “material use of wood should be prioritized over energy use of wood”, which forms the basis for our analysis herein. This working paper aims to inform the debate on cascading through an analysis of the terminology around cascading, and a review of how the concept is framed and implemented in policies of the EU and selected member states. It also discussed potential implications on international bioenergy markets from implementation of the cascading principle. The presentation of this study can also be found here.
YEAR 2015

Possible effects of torrefaction on biomass trade
Download | Low-cost preconditioning technologies of raw biomass that can convert and modify different sources of solid biomass into a specification-driven bioenergy feedstock with similar or even better characteristics as coal could greatly enhance trade and usage of biomass in the existing transportation and conversion infrastructure. A mild pyrolysis process called torrefaction stands out as a very promising technological option, attracting significant interest and financial resources for further technological development and commercialization. Torrefaction is these days on the verge of commercialisation. Beside a sheer volume of scientific studies, engineering initiatives not only a number of demonstration plants but now also first commercial plants are in operation respectively construction. The torrefaction technology seems to have left the valley of death behind, not without losses only in the adventurers but even in respectable companies and investors, and the current development leaves little doubt that this technology will find its way into the biomass-to-energy value chain in the next years. This study focuses on the possible effects torrefaction may have on future international biomass trade.
YEAR 2014

Ecological sustainability of wood bioenergy feedstock supply chains: Local, national and international policy perspectives
Download | The report first provides a brief overview of development of policy and criteria related to sustainability of bioenergy in the EU and in key biomass importer Member States (United Kingdom, the Netherlands and Belgium). The following sections then provide an thorough review of policy, regulations and practices of Canada and the United States, with a special focus of key biomass producing provinces/states (British Columbia, Ontario and Quebec in Canada, Georgia, New York and Massachusetts and California in the US); this in-depth analysis of the Canadian and American contexts was made possible due to the abundance of information available for those countries, but was also found necessary due to the scarcity of syntheses on this information. The next section then provides an overview of the policy and practices for land and forest management in Russia, with a focus on the region of Northwest Russia, based on the information that was possible to gather from this area. The report concludes with a discussion and main conclusions stemming from the analysis of the case studies.

Biomethane – Status and Factors Affecting Market Development and Trade
Download | A new report, “Biomethane: Status and Factors Affecting Market Development and Trade”, published in September 2014, was prepared jointly by Task 40 and Task 37 to address the status and emerging challenges of dealing with the rapid growth of production of biomethane, by either anaerobic digestion or thermal gasification, the developing biomethane market and trade of the gaseous biofuel. The aim of this study is to provide an up-to-date overview of the status of biomethane (including upgraded biogas and bio-SNG) production, grid injection and use in different countries, and to illustrate the options and needs for the development of larger biomethane supply strategies. The focus is on technical, economic and management- related hurdles to inject biomethane into the natural gas grid and to trade it transnationally. The study provides insights into the current status of technologies, technical requirements and sustainability indicators as well as cost of biomethane production and use in general and especially in selected countries. It also assesses implementation strategies, market situations and market expectations in selected countries, and proposes actions to be taken to reduce barriers and to develop the market step-by-step.
 Impact of promotion mechanisms for advanced and low-iLUC biofuels on markets
Impact of promotion mechanisms for advanced and low-iLUC biofuels on markets
With current discussions on indirect effects of biofuels, and the aim to broaden feedstocks to non-food biomass, policies are trying to put focus on biofuels from waste, residues and lignocellulose materials, so called ‘advanced’ biofuels. Next to the general biofuel incentives, these biofuels are getting extra support through specific promotion mechanisms. Examples are the double-counting mechanism for advanced biofuels in the EU, and the specific targets for advanced biofuels in the US. In this study, some typical cases are presented where promotion mechanisms for advanced biofuels have had an impact on markets and trade (used cooking oils and animal fats, sugarcane ethanol), or may be anticipated to impact markets and trade in the future (straw, wood pellets). General conclusions and summaries of the four case studies can be found in a summary report. Download summary.
The selected cases are:
1. Used cooking oils and animal fats for biodiesel: impact of the double-counting mechanism for advanced biofuels in the European Renewable Energy Directive on market prices and trade flows, analysed for the Netherlands and Italy. Download report
2. Sugarcane ethanol: impact of the subtargets for specific advanced biofuels in the US Renewable Fuels Standard (RFS2), where sugar cane ethanol is classified as ‘advanced biofuel’. This has had a clear impact on prices and trade patterns between Brazil and the US. Download report.
3. Crop residues (straw) for bioenergy: straw may play an important role for advanced biofuels in the future. In countries such as Germany, Denmark or Poland, this is an emerging feedstock for energy and biofuels. There are already some experiences we can take into account from the promotion of straw for stationary energy, e.g. in Denmark. Download report.
4. International trade of US wood pellets for bioenergy in the EU: Renewable Energy promotion in certain EU Member States is causing considerable trade flows from the US to the EU. There is clear that there are interactions with existing wood markets and forestry practises. In the future there may be additional effects when demand for cellulose-based biofuels enters these markets. Download report.
YEAR 2013

The transatlantic trade in wood for energy: A Dialogue on Sustainability Standards and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Download | The Savannah workshop was a unique opportunity to bring together a broad spectrum of stakeholders to evaluate sustainability issues – particularly biomass sourcing options – at a critical moment in the development of the global wood pellet trade. A key objective was to increase the collective understanding of sustainable procurement options already in use in the South and how these systems match up to European demand. Connections among participants were strengthened for future cooperation in hopes of establishing meaningful sustainability criteria. These connections are key to informing ongoing processes such as the deliberations of the Sustainable Biomass Partnership and governmental bodies throughout Europe and North America.
 Sustainable Biomass and Bioenergy in the Netherlands – Country Report 2013
Sustainable Biomass and Bioenergy in the Netherlands – Country Report 2013
Download | NL Agency commissioned Utrecht University’s Copernicus Institute, leader of the IEA Bioenergy Task 40 workgroup on biomass trade, to perform the analyses for this year’s annual report on Dutch biomass trade. The detailed report reviews the entire biomass arena as perceived from the Dutch context. Distinguishing between wood-based biomass flows, oils and fats and carbohydrates, and with much attention paid to the current push towards certification, the report is a must-read for all those involved in the biomass arena at the strategic level. The editors also provide an extensive framework for the monitoring and providing guidance to the growing biomass industry.
EU in the spotlight: New in this edition is an attempt at a comparative review of global imports and exports for ten leading commodities – with an emphasis on comparative data concerning the EU. The report shows that the EU continues to be a champion of biofuels and biomass imports, surpassing the US in imports of biodiesel and wood pellets. Link the news.
 Large Industrial Users of Energy Biomass
Large Industrial Users of Energy Biomass
Download | The objective of the study is to obtain a global overview of the biomass use in industrial and transport sectors and to compose lists of the largest users of energy biomass in the world. Various statistics, databases, reports, and reviews, most of them publicly available, have been utilised during the study to examine plants that either refine biomass for use in transportation and heating purposes or plants that convert biomass into heat and power. The plant lists presented are based on the prevailing situation in the end of the year 2012; due to lack of comprehensive and accurate plant-specific information and rapidly changing situation, the results should be used with care.
 Future Perspectives of International Bioenergy Trade
Future Perspectives of International Bioenergy Trade
Download summary | This study aims to provide insight into “possible futures” of bioenergy trade and discuss implications and challenges related to different developments. The sub-objectives of this study are:
– Investigate to which extent various global energy models and scenarios take into account bioenergy trade,
– Identify the implications of different global bioenergy scenarios on bioenergy trade,
– Summarize the range of results into 3-5 storylines of future international bioenergy trade.
The insight into future scenarios and perspectives of bioenergy trade revealed that substantial challenges for the future development of global and international bioenergy trade may be expected in the coming decades if a low carbon energy system is to be developed. The theoretical and technical biomass potentials in many models are often quite optimistic, and sustainable biomass potentials are only included to a limited extent, as these are often hard to quantify and are also not the main aim of the models. It remains to be seen how global, stringent mandatory sustainaibility requirements (e.g. on water use, biodiversity, forest carbon accounting and iLUC) would limit the production, trade and use of feedstocks in the first place, but also how practical certification of biomass would affect bioenergy trade
 Low cost, Long Distance Biomass Supply Chains (Revised in April 2014)
Low cost, Long Distance Biomass Supply Chains (Revised in April 2014)
Download | This report focuses on long-distance biomass supply chains, including ground-based supply of raw biomass to densification plants, and transportation of densified biomass to ports in other continents. It aims to: (i) provide an overview of the characteristics of three densified biomass forms; solid wood pellets, solid torrefied wood and liquid pyrolysis oil; for these; (ii) outline existing and future markets and specific supply chains for these products and explore large sources of biomass worldwide, some well-established and already being developed either for local use or trade, some only identified as a possible future potential source; (iii) highlight the importance of the costs of logistics in biomass supply chains; (iv) illustrate current cost structures of existing long-distance biomass supply chains, and (v) explore how the cost of current and future long-distance supply chains of wood pellets, torrefied pellets and pyrolysis oil could be lowered, and what this would require form the stakeholders involved.
 The Science-Policy Interface on the Environmental Sustainability of Forest Bioenergy
The Science-Policy Interface on the Environmental Sustainability of Forest Bioenergy
This publication reports on the discussions and opinions expressed during an expert workshop on the environmental sustainability of forest bioenergy in Canada, held in Quebec on the 3-5 October 2012.
The workshop was organised by the International Energy Agency Bioenergy Task 40 (International Sustainable Bioenergy Trade) and Task 43 (Biomass Feedstocks for Energy Markets), the IEA Bioenergy Executive Committee, the Faculty of Forestry, Geomatics and Geography of Laval University (Quebec, Canada), and Natural Resources Canada, with collaboration from the Global Bioenergy Partnership and the Canadian Council of Forest Ministers. Participants engaged in dialogue critical for the formulation of rational policy to achieve sustainable forest bioenergy production systems.
 Book: International Bioenergy Trade: History, status & outlook on securing sustainable bioenergy supply, demand and markets
Book: International Bioenergy Trade: History, status & outlook on securing sustainable bioenergy supply, demand and markets
The trade of global bioenergy commodities, such as ethanol, biodiesel and wood pellets has been growing exponentially in the past decade, and have by 2013 reached true “commodity” volumes, i.e. tens of millions of tonnes traded each year, and billions (both in US$/EUR) of annual turnover. IEA Bioenergy Task 40 was founded in 2004 and is now in its 4th triennium. For the past 9 years, task 40 has monitored the developments in international bioenergy trade, including the organization of about 20 workshops on trade-related topics, and the publication of over 100 studies, country reports, newsletters, etc. The amount of material produced over the years and insights gained in how biomass markets and international trade of biomass and biofuels has developed is impressive. Besides that the group has produced overviews and insights, also a large amount of practical experience has been brought together in what works and what doesn’t. Last but not least, based on all this, there are clear(er) views on how to proceed to build working sustainable international biomass markets in the future. This book compiles those lessons and insights into an easily accessible book publication. More information on the book available at Springer website.
 Monitoring Sustainability Certification of Bioenergy
Monitoring Sustainability Certification of Bioenergy
At present numerous biomass and biofuel sustainability certification schemes are being developed or implemented by a variety of private and public organisations. This induces multiple challenges, e.g. confusion among actors involved, fear of market distortion and trade barriers, an increase of commodity costs, questions on the adequacy of systems in place and uncertainty over how to develop systems that are effective and yet cost-efficient. To support sustainable bioenergy deployment and overcome some of the challenges mentioned above, this IEA Bioenergy strategic study examined what is actually known and what can be learned from the current development and implementation of voluntary certification systems, about the role of voluntary certification schemes in the governance of biomass/bioenergy/biofuels sustainability and how this has affected actors along the supply chains and trade. Download short summary.
The study has produced four reports,
1. Examining sustainability certification of bioenergy (task 1) Download
2. Survey on governance and certification of sustainable biomass and bioenergy (task 2)
3. Impacts of sustainability certification on bioenergy markets (task 3) Download
4. Recommendations for improvement of sustainability certified markets (task 4) Download
YEAR 2012
 Possible effect of torrefaction on biomass trade
Possible effect of torrefaction on biomass trade
Download | 14 November 2012 – The focus of this study is to examine briefly the status of the development of torrefaction technology, and more importantly assess what are the likely biomass sources and what impact the development of torrefied wood will have on global trade, in particular between now and 2020. This study assessed the extent torrefaction might open up new biomass feedstock sources, and explored how torrefied biomass will perform along the logistical chain of long-haul international transport and at the end-use conversion plants. The torrefaction process was compared with two other important preconditioning technologies: simple pelletization and flash pyrolysis. Another report by Task 32, “Status overview of torrefaction technologies“, presents an overview of the current status of torrefaction technologies and their market perspectives.

The Potential Role of Biofuels in Commercial Air Transport – Biojetfuel
Download | 11 August 2012 – This report is an overview, not a detailed analysis, of the use of biofuels in commercial aviation. Aviation is a global industry with global problems and challenges that also demands global solutions. Key objectives of commercial aviation are to find reliable fuel alternatives to cut costs, and reduce volatility of fuel supply, GHG and improve logistics. The use of biofuels in commercial aviation has received considerable attention in recent years, as it is currently one of the best short to medium term alternatives. Commercial aviation is predicted to grow at a 5% rate annually until 2030, exceeding expected fuel efficiency improvements of approximately 3%; this implies that fuel consumption and emissions will continue to rise. According to IATA (2011b) the airline industry will progress from carrying 2.4 billion passengers in 2010 to an estimated 16 billion passengers in 2050. The global fleet now numbers 100,000 and there are eight major aircraft manufacturers. This is an industry that requires huge investment but provides low returns. See report for more details.

Global Wood Chip Trade for Energy
Download | 8 June 2012 – This report has been commissioned to identify and present global data on wood chip trade, to analyze the underlying trade patterns, and to conclude upon their interactions with bioenergy policies. At the centre of the analysis is direct trade of wood chips for modern bioenergy use in markets where respective policies are in place. Whereas associated trade flows where the initial reason is not directly related to energy usage, e.g., wood chips for pulp and paper of which a fraction ends up as black liquor and is used for energy (see ref [8] in the report for a distinction in the case of Finland) are outlined to put the energy related trade into perspective, but not investigated in detail.
Prospective study: Implementation of sustainability requirements for biofuels and bioenergy and related issues for markets and trade
Download | 9 February 2012 – The thesis explores global and national-level issues related to the development of markets for biomass for energy. The thesis consists of five separate papers and provides insights on selected issues. The aim of Paper I was to identify methodological and statistical challenges in assessing international solid and liquid biofuels trade and provide an overview of the Finnish situation with respect to the status of international solid and liquid biofuels trade. The purpose of Paper II was to provide a quantified insight into Finnish prospects for meeting the national 2020 renewable energy targets and concurrently becoming a largescale producer of forest-biomass-based second-generation biofuels for feeding increasing demand in European markets. Paper III summarises the global status of international solid and liquid biofuels trade as illuminated by several separate sources. The objective of Paper V was to clarify the alternative scenarios for the international biomass market until 2020 and identify the underlying steps needed toward a wellfunctioning and sustainable market for biomass for energy purposes.
YEAR 2011
 Global Wood Pellet Industry Market and Trade Study (Most downloaded)
Global Wood Pellet Industry Market and Trade Study (Most downloaded)
Download | December 2011 – The wood pellet market has experienced a large growth in the last five years (2006-2011). In 2006 the production of wood pellets was estimated between 6 and 7 million tonsworldwide (not including Asia, Latin America and Australia), drawn from a previous Task 40 pellet market study published in 2007. In 2010 the global wood pellet production reached 14.3 million tons, including the above mentioned countries, while the consumption was close to 13.5 million tons thus recording an increase of more than 110% if compared to 2006. This report presents the wood pellet industry and market in Europe and North America. It also includes perspectives of domestic use and trade of wood pellets in emerging markets (Asia and Latin America) and the challenges to ensure a sustainable pellet trade.A shortened version of this report has been published by BioFPR: C.S. Goh, M. Cocchi, M. Junginger, D. Marchal, D. Thran, C. Hennig, J. Henimo, L. Nikolaisen, P.P. Schouwenberg, D. Bradley, R. Hess, J. Jacobson, L. Ovard, M. Deutmeyer (2013) Wood pellet market and trade: A global perspective. Biofuels, Bioproducts, and Biorefining. 7(1), p.24-42.
Development of a tool to model European biomass trade – Report for IEA Bioenergy Task 40
Download | November 2011 – This report presents the results of an effort for IEA Bioenergy Task 40 to develop a modelling tool for international biomass trade. Part of this work has also been done in the frame of the RE-Shaping project, and parts of the methodology and the results have also been published as a RE-Shaping deliverable (Hoefnagels, Junginger et al. 2011). In addition, the scenarios for International solid biomass imports were originally developed for the European Commission (Junginger, 2011). The main aim of this report is to illustrate the approach to include logistic cost of biomass in an energy model and implications to supply and demand of biomass for bioenergy. The costs, as presented in this report, are not intended to and do not always reflect actual (fluctuating) prices of feedstocks, pre-processing and transport of bulk freight.
Summary, synthesis and conclusions from IEA Bioenergy Task 40 country reports on international bioenergy trade
Download | April 2011 – Based on the experiences in the Task 40 member countries, this report [252 KB] shows how bioenergy trade has developed during the past 6 years in the member countries, and how it has contributed to increasing bioenergy production and utilisation. Between 2004 and 2007, the absolute amount and share of bioenergy in the total primary energy supply has increased in all countries except for Canada, the US and Norway. In some countries, the increase has been substantial, e.g. doubling in Belgium and Germany. International bioenergy trade has played an important role in this increase: summed up over all Task 40 countries, the total trade volume of both imports and exports has increased by about a factor of 2 between 2004 and 2007. The increase was mainly due to a strongly rising trade in liquid biofuels (164% increase in total imports, 172% increase in exports), while the trade in solid biomass increased more moderately but still significantly (51% and 16%). More details, including policy and market drivers and concise descriptions of the developments in each member country are also included in the report.
YEAR 2010
Opportunities and barriers for international bioenergy trade
Download | May 2010 – The aim of this report is to provide up-to-date overview of what market actors currently perceive as major opportunities and barriers for the current and future development of international bioenergy trade. The work focuses on three internationally traded bioenergy commodities: bioethanol, biodiesel and wood pellets. Data was collected through an internet-based questionnaire, which was completed by 141 respondents. Results show that import tariffs and sustainability criteria are perceived as major barriers for the trade of bioethanol (and to a lesser extend of biodiesel), while logistics are seen as an obstacle mainly for wood pellets. Development of technical standards was deemed more as an opportunity than as a barrier for all three commodities. Phytosanitary measures were not an issue for any of the investigated commodities, but may prevent the trade of other (mainly solid and unrefined) biomass, such as wood chips. Most important drivers were high fossil fuel prices and climate change mitigation policies. Concluding, some barriers for bioenergy trader are commodity specific, and will need specific actions to overcome. As a first step, import tariffs for biofuels could be reduced or abolished, linked to multi-national trade agreements and harmonization (including provisions on technical standards and sustainability requirements) which might provide the necessary preconditions for further sustained growth of international bioenergy trade. A shortened version of this report has been published by Energy Policy. This background report contains additional information, including the original survey and all answers provided by the respondents. Preferably, please use the following reference for citation: Junginger, M., van Dam, J., Marchal, D., Faaij, A., Zarrilli, S., Ali Mohamed, F., (2011) Barriers and opportunities for global bioenergy trade, Energy Policy 39 (2011) 2028-2042, doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2011.01.040
Updated overview of bioenergy sustainability certification initiatives published
Download April 2010 – The report includes an extensive overview and update on relevant certification initiatives and systems for biomass and bioenergy certification, based on the year of 2009. Examples of included initiatives are the roundtable initiatives (RSB, RTRS, BSI, etc), forestry standards (FSC, PEFC), agricultural standards (SAN, GlobalGAP) and specific voluntary standards for bioenergy (ISCC, NTA8080). Every initiative gives a description of the context, status and organization structure. This is followed by a description of its principles, criteria and indicators. The report is the background document from the paper Dam et al (2010), From the global efforts on certification of bioenergy towards an integrated approach based on sustainable land use planning (submitted to the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews). This article provides a comparison between the systems, followed by an overview of current bottlenecks, and required activities, to come to a harmonized, efficient system to guarantee the sustainability of biomass and bioenergy.
World Bio-trade Equity Fund Study
Download | 18 April 2010 – Investing in bioenergy (and especially in bioenergytrade) is not generally well understood in the investment community. The objective of this study was to explore the possibility for the creation of a Bio-trade Equity Fund. Such a fund could be to invest in projects that promote world trade in biomass while yielding a rate of return commensurate with risk. Projects could include: improving ground-based biomass feedstock supply systems, such as advanced chipping systems and inland ships; building biomass conversion plants, such as for pellets, BioOil, 2nd generation ethanol and torrefied wood; and enhancing bio-product transportation systems, such as port improvements, purpose built loaders, and specialized biofuel ships. The study concludes that such a fund could be feasible, and outlines a possible business plan, including the setup of the fund, a time schedule and example projects a fund could invest in. It is anticipated that such a fund could result in meaningful volumes of biomass transported where they are needed most in the next 10 years to achieve renewable fuel targets. It in turn would result in the creation of jobs in developing nations, commercialization of new technologies, and ultimately reduction in worldwide GHG emissions. In case you would like to receive more information, please contact the main author of the study, Doug Bradley.



